Search

Search











Tauroursodeoxycholic acid is mainly used for the treatment of gallbladder cholesterol stones, primary sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and chronic viral hepatitis C.
Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid can reduce the secretion of cholesterol by the liver, reduce the saturation of cholesterol in bile, promote the secretion of bile acids, increase the solubility of cholesterol in bile, dissolve cholesterol stones or prevent the formation of stones. STauroursodeoxycholic Acid in bowurs can increase bile secretion, relax the sphincter of the bile duct to produce choleretic effect, and facilitate the expulsion of stones.
| Items | Specification | Result |
| Assay | ≥98% | 99.3% |
| Apperance | White crystals | White crystals |
| Heavy metals | ≤20ppm | <20ppm |
| Related substances | UrsodeoxycholicAcid≤0.5% Taurochenodeoxycholic acid≤0.8% Other Impurity≤0.4% Total of any other impurities≤1.0% | Pass Pass Pass Pass |
| Moisture | 6.5%-7.5% | 7.1% |
| Sulphated ash | ≤0.1% | 0.03% |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 14605-22-2 |
| Appearance: | White crystals |
| Purity: | 98%min |
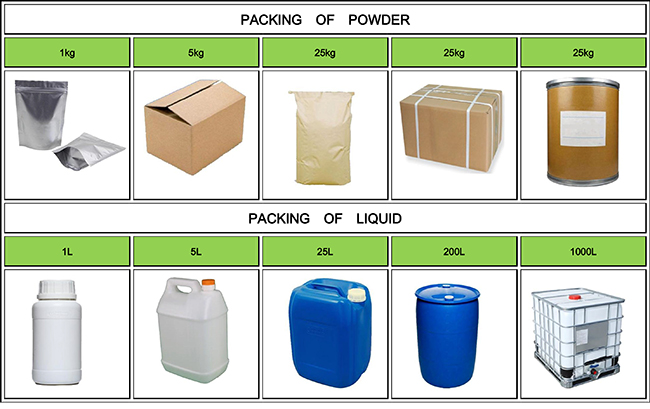
| Package details: | 1kg/foil bag;25kg/drum |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) is a water-soluble bile acid amide. Chemically, it is the taurine conjugate of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). This means it is formed by combining UDCA (a secondary bile acid) with the amino acid taurine via an amide bond.
Key Chemical Characteristics:
Chemical Formula: C₂₆H₄₅NO₆S
Solubility: It is much more water-soluble than its parent compound, UDCA, due to the presence of the strongly polar sulfonic acid group from taurine.
Nature: It is a naturally occurring bile acid in small amounts in humans and in larger amounts in bears (hence "urso-," from Ursidae, the bear family). It is now produced synthetically for commercial and research use.
While TUDCA has gained significant attention in medicine, its uses stem from its fundamental chemical and biochemical properties. Here’s a breakdown from a chemical perspective:
This is its most studied and important chemical property.
Mechanism: TUDCA is a chemical chaperone. It helps proteins achieve and maintain their correct three-dimensional (native) folding, especially under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress.
Chemical Action: It stabilizes protein structure, inhibits protein aggregation (clumping of misfolded proteins), and promotes the proper trafficking of proteins within cells. It does this by interacting with the protein folding machinery and the lipid bilayer of cell membranes.
Why it Matters: Misfolded proteins are central to many diseases. By chemically assisting proper folding, TUDCA counteracts a key pathological process.
Mechanism: Due to its amphiphilic structure (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts), TUDCA integrates into cell membranes.
Chemical Action: It modulates membrane fluidity, protects mitochondrial membranes, and inhibits the release of pro-apoptotic (cell death-inducing) factors like cytochrome c. This makes it a potent cytoprotective (cell-protecting) agent.
Mechanism: It interferes with key chemical pathways of programmed cell death (apoptosis).
Chemical Action: It inhibits upstream triggers of apoptosis (like ER stress) and modulates the activity of key proteins (e.g., Bax, Bcl-2) involved in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.
Mechanism: It chemically modulates signaling pathways (like NF-κB and JNK) that drive inflammation and oxidative stress.
Chemical Action: It reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines.
Based on these chemical properties, TUDCA is investigated and used for:
Hepatoprotective Therapy: Used to treat certain cholestatic liver diseases (e.g., primary biliary cholangitis) by protecting liver cells from toxic bile acids and reducing inflammation.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Extensive research in models of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease, and ALS, due to its ability to reduce ER stress and protein aggregation in neurons.
Retinal Diseases: Used in ophthalmology for retinal disorders like retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy, protecting light-sensitive cells from apoptosis.
Metabolic Disorders: Studied for type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance, as ER stress plays a role in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction.
Stroke and Neuroprotection: Shown to reduce brain cell death and improve outcomes in animal models of ischemic stroke.
Tool Compound: Ubiquitously used in cell biology and molecular biology labs as a standard agent to inhibit ER stress-induced apoptosis. It's a key tool for studying cellular stress pathways.
Protein Folding Studies: Used in biochemistry research to understand protein misfolding diseases and screen for other chaperone molecules.
Available as a supplement, primarily marketed for liver support, neuroprotection, and as an ergogenic aid. However, the quality, efficacy, and safety for off-label uses are not as rigorously regulated as for pharmaceutical-grade TUDCA.
UDCA vs. TUDCA: UDCA (ursodeoxycholic acid) is the more common pharmaceutical for liver conditions. TUDCA is its more water-soluble, potent conjugate. The taurine moiety enhances its solubility, membrane interaction, and chaperone activity, making it often more effective in experimental models, especially for non-liver conditions like neurological disorders.
In essence, Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid is a chemically defined, amphiphilic bile acid whose value lies in its fundamental properties as a chemical chaperone and membrane stabilizer. These properties translate directly into its primary uses as a hepatoprotective drug, a leading neuroprotective research compound, and an essential laboratory reagent for studying cellular stress.



Guaranteed purity
High quality & competitive price
Quality control
Fast feedback
Prompt shipment

Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية