Search

Search











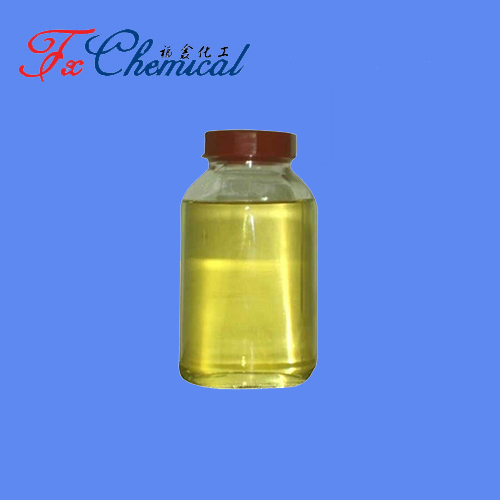
Potassium metabisulfite (K₂S₂O₅) is a white, crystalline powder used primarily as a preservative and antioxidant. It releases sulfur dioxide (SO₂), which inhibits microbial growth and prevents browning in food and beverages. It is widely used in winemaking and brewing to sanitize equipment and stabilize products. Commonly found in dried fruits, juices, and wines, it must be labeled as "contains sulfites," as it can cause allergic reactions, especially in asthmatics. Handling requires care, as the powder is a strong respiratory irritant and should not be inhaled.
Potassium metabisulfite (K₂S₂O₅) is an inorganic chemical compound, a white crystalline or powdered substance with a pungent, sharp sulfurous odor (like struck matches). It is a potassium salt of metabisulfurous acid.
It is a powerful preservative, antioxidant, and sterilizing agent widely used in several industries, most notably in food and beverage production and winemaking.
Its efficacy comes from its ability to release sulfur dioxide (SO₂) when dissolved in water or acid. Sulfur dioxide is the active agent responsible for all its effects:
Antioxidant: It prevents oxidation (browning) in foods and beverages by scavenging oxygen. This protects color, flavor, and aroma.
Antimicrobial: It inhibits the growth of bacteria, wild yeasts, and fungi (like mold), thereby preventing spoilage and unintended fermentation.
Antiseptic: It is used to sanitize equipment (like brewing barrels and bottles) to kill unwanted microorganisms.
1. Winemaking and Brewing (Most Famous Use)
Sanitizer: Used to sterilize equipment, barrels, and bottles to prevent microbial contamination.
Preservative: Added to wine, beer, cider, and mead after fermentation to prevent oxidation and stop any remaining yeast or bacteria from spoiling the product. It stabilizes the beverage for aging.
To halt fermentation: In sweet wines, it can be used to stun or kill yeast, leaving residual sugar.
2. Food Industry
Preservative: Found in a wide variety of processed foods, often listed on ingredient labels as E224 (its E number in Europe). Examples include:
Dried fruits (to retain color and prevent mold)
Fruit juices and concentrates
Wine vinegar
Processed potatoes (e.g., dehydrated potato flakes)
Some maraschino cherries
Antioxidant: Prevents browning in raw, pre-cut fruits and vegetables (like the apples in pre-made salads).
3. Other Uses
Pharmaceuticals: Used as a preservative in some medications.
Photography: A component of some photographic developing solutions.
Textile Industry: Used as a bleaching agent.
While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory bodies like the FDA when used in approved amounts, it requires careful handling.
1. For Consumers:
Asthma and Sulfite Sensitivity: This is the most significant concern. Potassium metabisulfite can cause severe allergic-like reactions in asthmatics and sulfite-sensitive individuals. Reactions can range from wheezing and difficulty breathing to anaphylactic shock in very rare cases. For this reason, its use in fresh foods (like salad bars) is heavily restricted, and products containing significant sulfites (>10 ppm) must be labeled with warnings like "Contains Sulfites."
General Public: For most people, consuming it in regulated amounts in food and wine is considered safe.
2. For Handlers (Homebrewers, Industry Workers):
Inhalation Hazard: The powder is a serious respiratory irritant. It should never be inhaled directly, as it can cause bronchospasm, coughing, and shortness of breath. It must be used in a well-ventilated area.
Skin and Eye Irritant: It can cause irritation upon contact. Safety glasses and gloves are recommended when handling the pure powder.
They are functionally very similar—both release sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and perform the same roles. The choice between them often comes down to:
Sodium Content: Potassium metabisulfite is preferred by those wishing to avoid adding sodium to their diet or product (e.g., in "low-sodium" wines).
Potassium Content: In very high doses, it can contribute a slightly bitter or salty taste compared to its sodium counterpart.
Solubility: Potassium metabisulfite is slightly less soluble in water than sodium metabisulfite.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | A white, crystalline powder with the formula K₂S₂O₅. |
| Primary Function | A source of sulfur dioxide (SO₂), acting as a preservative, antioxidant, and antimicrobial agent. |
| Most Common Use | Sanitizing and preserving agent in winemaking, brewing, and food processing. |
| E Number | E224 |
| Key Safety Concern | Can trigger severe asthma attacks in sulfite-sensitive individuals. |
| Handling Warning | Do not inhale the powder; it is a potent respiratory irritant. |
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Always follow safety data sheets (SDS) when handling chemicals and heed product warnings regarding sulfite content.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية ![Dichloro-[2,2]-paracyclophane CAS 28804-46-8 Dichloro-[2,2]-paracyclophane CAS 28804-46-8](/uploads/file/20220615/10/dichloro-22-paracyclophane-cas-28804-46-8.webp)
ETHANOL主图.jpg)





