Search

Search










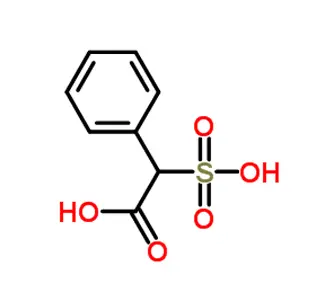
Azilsartan Impurity 16 is a specified degradation product or synthetic byproduct identified during the manufacturing or storage of Azilsartan medoxomil, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used to treat hypertension. It is structurally related to the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) but differs due to unintended chemical modifications during synthesis or decomposition. Regulatory bodies like the ICH mandate strict control of such impurities to ensure drug safety and efficacy. While its exact structure may vary, it typically arises from incomplete reactions, isomerization, or oxidation of intermediates. Analytical methods (e.g., HPLC, LC-MS) are used to quantify it, adhering to limits set by pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP, EP). Proper identification is critical for quality control.
Azilsartan Impurity 16 is a identified byproduct or degradation product associated with the synthesis or storage of Azilsartan medoxomil, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used to treat hypertension. Here's a structured summary:
Origin:
Likely arises during the synthesis of Azilsartan medoxomil (e.g., incomplete reactions, side reactions, or intermediates) or from degradation (e.g., hydrolysis, oxidation, or exposure to light/heat).
Structural Characteristics:
While the exact structure isn't specified here, impurities in ARBs like Azilsartan often relate to modifications in the tetrazole ring, ester group (medoxomil moiety), or substituents. It could be a positional isomer, dimer, or derivative with altered functional groups.
Regulatory Context:
Governed by ICH guidelines, impurities must be identified, quantified, and controlled if they exceed thresholds (typically ≥0.1% of the drug substance). Regulatory filings (e.g., FDA NDA, EMA reports) detail such impurities to ensure safety.
Analytical Control:
Characterized using techniques like HPLC, LC-MS, or NMR. Manufacturers monitor its levels to comply with pharmacopeial standards (USP, Ph. Eur.) and ensure it remains within safe limits.
Significance:
Critical for drug quality and patient safety. Even non-toxic impurities must be controlled to avoid batch variability or stability issues.
For the precise structure or toxicological profile, consulting Azilsartan’s drug master file, FDA/EMA assessment reports, or peer-reviewed studies would be necessary. These sources often provide chemical names, structural diagrams, and synthesis pathways for listed impurities.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية