Search

Search
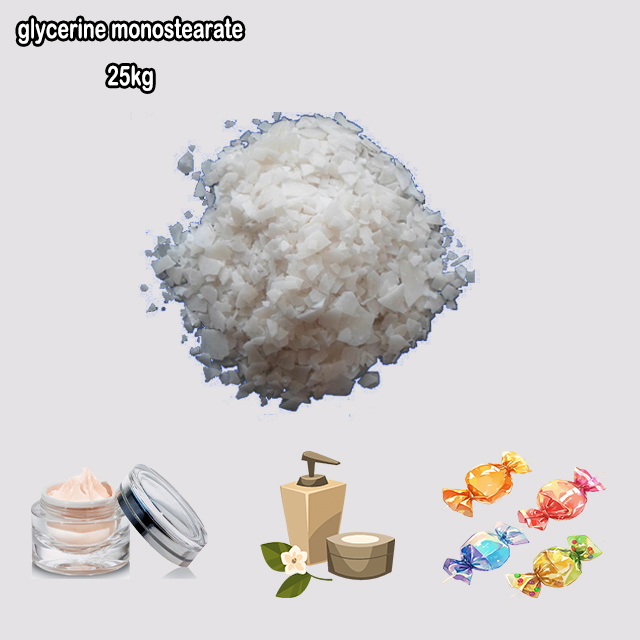











Glycerine monostearate (GMS) is a monoglyceride emulsifier, formed from glycerol and stearic acid (a C18 fatty acid). As an amphiphilic molecule, it acts as a surfactant, enabling the mixing of oil and water.
It is widely used as a food additive (E471) in products like ice cream, bread, and whipped toppings to improve texture, stability, and shelf life. In cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, it serves as an emulsifier, thickener, and emollient in creams, lotions, and tablets. It is generally plant or animal-derived and considered safe.
Glycerine monostearate (GMS), also known as monostearin, is a monoglyceride. It is an ester formed when one molecule of stearic acid (an 18-carbon saturated fatty acid) binds to one of the three hydroxyl groups of a glycerol molecule.
Its key property is being an effective non-ionic surfactant and emulsifier. This means it has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head from the glycerol and a lipophilic (fat-attracting) tail from the stearic acid chain. This allows it to stabilize mixtures of oil and water, preventing them from separating.
Primary Applications:
Food Industry (Additive E471): The most common use. It acts as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and thickening agent in products like ice cream, bread, whipped cream, and shortening to improve texture, volume, and shelf life.
Cosmetics & Personal Care: Used as an emulsifier in creams and lotions, an opacifying agent to make products opaque, and an emollient to soften the skin.
Pharmaceuticals: Serves as a tablet lubricant, binder, and controlled-release agent in solid dosage forms.
It can be derived from plant (e.g., palm, soybean) or animal fats and is generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
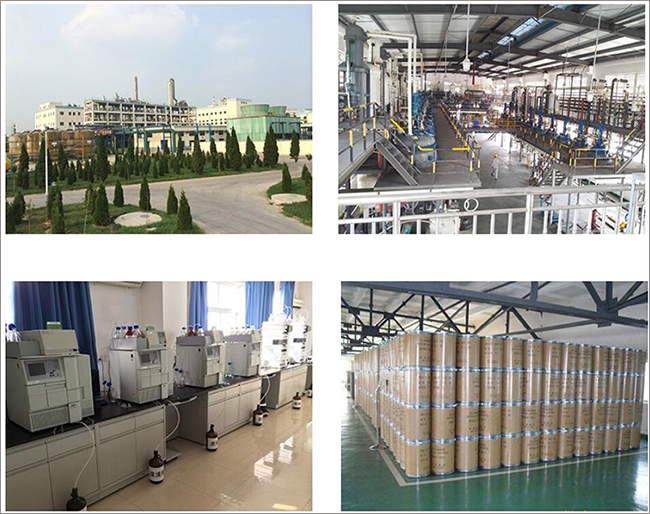



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 






