Search

Search











Oleanolic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid, widely found in plants like olive leaves, cloves, and fruits. Its core structure consists of five fused rings (oleanane skeleton).
Key chemical features include:
A carboxylic acid group at position C-28.
A hydroxyl group (-OH) at position C-3 (typically β-configuration).
A characteristic double bond between C-12 and C-13.
Molecular Formula: C₃₀H₄₈O₃.
It serves as the aglycone (non-sugar part) for many saponins and exhibits diverse biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, and potential anticancer effects. It is a structural isomer of ursolic acid.
Oleanolic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid with the following key chemical characteristics:
Chemical Classification:
Triterpenoid: Derived from six isoprene units (30 carbon skeleton).
Pentacyclic: Contains five fused rings in its core structure.
Oleanane-type: Specifically has the oleanane carbon skeleton (characterized by the arrangement of its rings and methyl groups).
Triterpenoid Saponin Aglycone (Sapogenin): It's the non-sugar part (aglycone) of many saponins found in plants.
Molecular Formula: C₃₀H₄₈O₃
Core Structure:
Five fused rings (designated A, B, C, D, E), forming the oleanane nucleus.
Standard configuration has rings A/B, B/C, C/D, and D/E trans-fused.
Key Functional Groups:
Carboxylic Acid: Located at position C-28 (attached to the E-ring). This makes it an acid and is crucial for many of its biological activities.
Hydroxyl Group: Located at position C-3 (on the A-ring). The standard stereochemistry is β (3β-hydroxy).
Methylene Group (-CH₂-): Characteristically found at position C-17 (connecting the D and E rings).
Stereochemistry:
The hydrogen at the C-3 hydroxyl group is typically in the β-position (pointing upwards relative to the ring plane).
The methyl groups at positions C-4, C-8, C-10, and C-14 are in the α-position (pointing downwards).
The methyl groups at positions C-17 are both α (one is part of the -CH₂- bridge).
Structural Isomerism:
Oleanolic acid has the methyl groups at positions C-19 and C-20 (E-ring) in a trans-fusion configuration.
Ursolic acid has them in a cis-fusion configuration (ursane skeleton).
Oleanolic acid is a structural isomer of Ursolic Acid. Both share the same molecular formula (C₃₀H₄₈O₃) and functional groups (COOH at C-28, OH at C-3β). The difference lies in the position of one methyl group:
Representation:
Simplified Structure: Often depicted showing the pentacyclic rings with the -CH₂- at C-17, the -COOH at C-28, and the -OH at C-3.
Skeletal Formula: The most common representation highlights the ring system and functional groups clearly. (You can easily find this by searching "oleanolic acid structure" online).
Natural Occurrence: Widely distributed in the plant kingdom, found in leaves, fruits, and roots (e.g., olive, clove, mistletoe, garlic, jujube, rosemary, honeysuckle).
In Summary: Chemically, oleanolic acid is a 3β-hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid. This systematic name precisely describes its structure: an oleanane skeleton with a double bond between C-12 and C-13 (standard position), a β-hydroxyl group at C-3, and a carboxylic acid group at C-28. Its CAS Registry Number is 508-02-1.
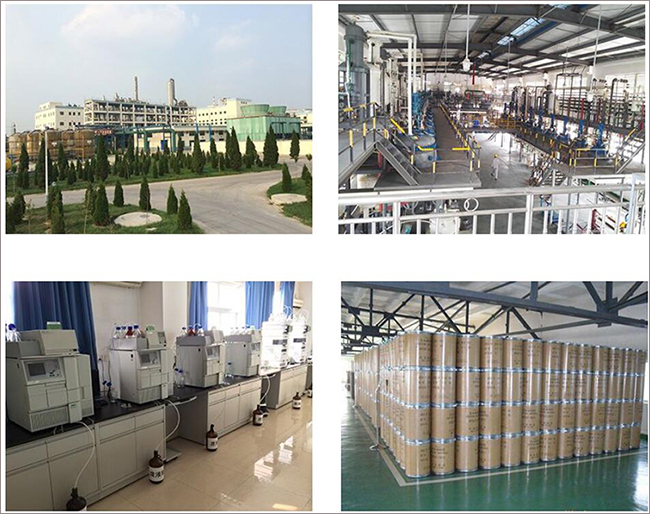



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 






