Search

Search











DL-Homocystine is the synthetic, racemic mixture of the sulfur-containing amino acid homocystine. Homocystine itself is formed when two molecules of homocysteine oxidize and connect via a disulfide (-S-S-) bridge.
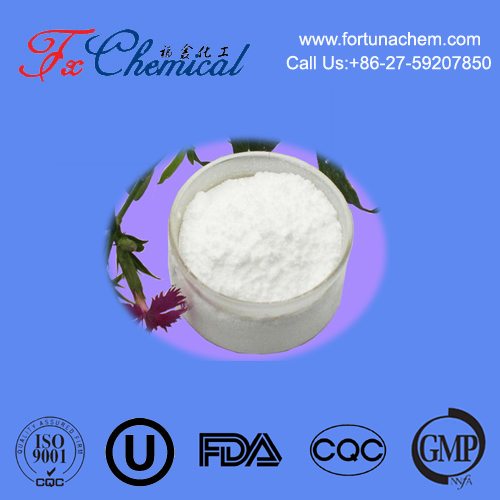
Key Properties: It is a white crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water. The "DL" prefix indicates it contains equal parts of the D- and L- stereoisomers. Only the L-form is biologically relevant.
Primary Use: It is not a natural dietary amino acid. Its main use is in biochemical research as a standard in analytical studies and as a precursor to investigate homocysteine metabolism, which is crucial for understanding conditions like cardiovascular disease and homocystinuria.
DL-Homocystine is the synthetic, racemic form of the amino acid homocystine. To understand this compound, it's best to break down its name and components:
Homocystine: This is a disulfide compound formed by the oxidation of two molecules of homocysteine. Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid and a key intermediate in methionine and cysteine metabolism. The linkage of two homocysteine molecules via a disulfide bond (-S-S-) creates homocystine.
"DL-" Prefix: This indicates that the compound is a racemic mixture. It contains a 50/50 blend of two mirror-image stereoisomers: D-homocystine and L-homocystine. The "L" form is the one that is biologically active and found in natural systems, while the "D" form is not metabolized by most biological enzymes.
Chemical Structure: It is a dimer of homocysteine connected by a disulfide bridge.
Appearance: Typically a white crystalline or powdered solid.
Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in water.
Biological Relevance: It is not a standard dietary amino acid found in proteins. Instead, it is primarily a metabolite and an oxidative product of homocysteine.
The sole significant use of DL-Homocystine is in the field of scientific and biochemical research. It is not used as a supplement or therapeutic agent.
Its main applications include:
Research Standard: It is widely used as a reference standard in chromatographic analysis (like HPLC and mass spectrometry) to identify, quantify, and study levels of homocysteine and homocystine in biological samples (e.g., blood plasma, urine). Accurate measurement is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring metabolic disorders.
Studying Homocysteine Metabolism: Researchers use DL-homocystine to investigate the biochemical pathways involving homocysteine, particularly the methionine cycle and the transsulfuration pathway.
Modeling Disease States: Elevated levels of homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia) are a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, thrombosis, and cognitive decline. DL-Homocystine is used in in vitro (lab-based) studies to induce and study the cellular effects of these conditions.
Investigating Homocystinuria: This is a rare genetic disorder where the body cannot properly process methionine, leading to a dangerous accumulation of homocystine and homocysteine. Research using this compound helps understand the disease mechanisms and potential treatments.
In summary, DL-Homocystine is a synthetic research chemical essential for scientists studying sulfur amino acid metabolism and its critical links to human health and disease. It serves as a vital tool in the lab rather than a compound with direct industrial or commercial applications.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 






