Search

Search











Acid Chrome Blue K (also known as Calcon) is a synthetic azo dye used primarily as a metallochromic indicator in analytical chemistry. It is essential for determining water hardness by complexometric titration with EDTA. The indicator binds to calcium and magnesium ions, forming a red complex. When all metal ions are sequestered by EDTA, it releases them and changes color sharply from red to blue, signaling the titration's endpoint. This clear visual change makes it a reliable tool for measuring total calcium and magnesium concentration in water.
Acid Chrome Blue K is a synthetic dye belonging to the azo dye class. Its primary historical use was as a metallochromic indicator in analytical chemistry, specifically for the complexometric titration of calcium and magnesium ions. It is also known by several other names, most commonly Calcon or Calcon Carboxylic Acid.
Its chemical name is Sodium 1-(2-Hydroxy-1-naphthylazo)-2-naphthol-4-sulfonate.
Class: Azo dye (characterized by the presence of the functional group R−N=N−R′).
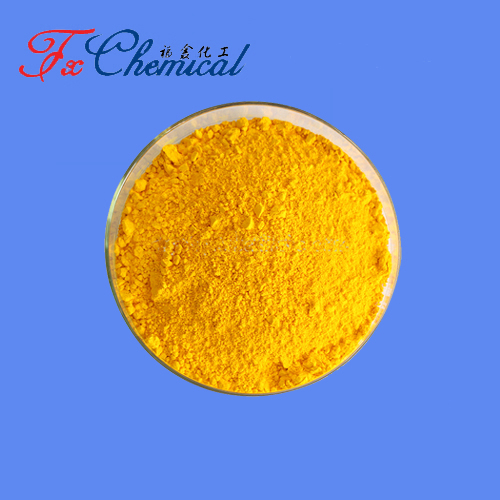
Appearance: It typically comes as a dark brownish-black or dark purple powder.
Solubility: It is soluble in water and ethanol, forming a deep blue or purple solution.
Metallochromic Indicator: This is its key property. It changes color upon binding to specific metal ions. In its free form (unbound to metal), it is typically blue. When it forms a complex with calcium (Ca²⁺) or magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions, it turns pink or red.
This is the most important application of Acid Chrome Blue K. It is used to determine the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in a water sample, which is a key measure of water hardness.
How it works in a titration with EDTA:
Preparation: The water sample to be analyzed is buffered to a pH of around 10 (using an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer). At this pH, both calcium and magnesium ions are available to react.
Addition of Indicator: A small amount of Acid Chrome Blue K is added to the solution. It immediately binds to some of the Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺ ions, forming a red complex.
Color in Solution: Red/Pink (indicates the presence of free Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺ ions).
Titration: A solution of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is slowly added from a burette. EDTA is a powerful chelating agent that forms even stronger, colorless complexes with Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺ than the indicator does.
Endpoint: As EDTA is added, it sequesters all the free metal ions in the solution. Once all the free ions are complexed, the EDTA then "steals" the metal ions from the metal-indicator (red) complex.
Color Change: The metal ion is removed from the indicator, which returns to its free form. This causes a sharp and clear color change from red to blue.
Color at Endpoint: Pure Blue (indicates all metal ions have been complexed by EDTA).
The point at which the color permanently changes from red to blue is the endpoint. The volume of EDTA used to reach this point is used to calculate the total concentration of calcium and magnesium ions in the sample, expressed as parts per million (ppm) of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
Specificity: It is used for the total hardness (Ca + Mg) and is not specific for either ion individually at pH 10.
pH Sensitivity: The titration must be performed at a high pH (~10) to ensure the EDTA reacts correctly and the color change is vivid.
While its use as an indicator is most classic, Acid Chrome Blue K has other applications:
Histological Staining: It has been used in biological staining techniques.
Dyeing: As a member of the azo dye class, it can be used to dye materials, though this is not its primary application today.
Like many synthetic chemical compounds, appropriate safety precautions should be taken:
It may cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract.
It should be handled in a well-ventilated area (or a fume hood for powders) using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses.
Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific product for detailed handling and disposal information.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | A synthetic azo dye and metallochromic indicator. |
| Common Names | Acid Chrome Blue K, Calcon, Calcon Carboxylic Acid. |
| Primary Function | Indicator for the complexometric titration of total water hardness (Calcium and Magnesium ions) using EDTA. |
| Color Change | Red (metal complex) to Blue (free indicator) |
| Key Application | Analytical chemistry, water quality testing. |
In essence, Acid Chrome Blue K is a crucial tool in analytical chemistry labs for determining water hardness, providing a clear and reliable visual signal for the endpoint of a titration.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 






