
Search

Search











Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) is an ionic compound of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
Properties:
Prepared by slaking lime (CaO + H₂O → exothermic).
Sparingly soluble; forms strongly alkaline solutions (limewater/milk of lime).
Reacts with CO₂ to form CaCO₃ (carbonation).
Key Uses:
Construction: Mortar/plaster binder.
Water Treatment: pH adjustment, flocculation.
Agriculture: Soil neutralizer ("lime").
Food: Additive E526 (pickling, corn processing).
Safety: Corrosive solid; wear protective gear. Rarely occurs naturally as portlandite.
Calcium hydroxide (chemical formula: Ca(OH)₂) is an inorganic compound composed of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Here's a concise chemical overview:
Formula & Structure:
Ionic compound with a 1:2 ratio of Ca²⁺ to OH⁻ ions.
Crystalline structure: Hexagonal plates (portlandite), layered lattice.
Preparation:Produced by slaking quicklime (CaO) with water:
CaO+H2O→Ca(OH)2(Highly exothermic)
CaO+HX2O=>Ca(OH)X2(Highly exothermic)
Solubility & Basicity:
Sparingly soluble in water (~0.173 g/100 mL at 20°C), forming an alkaline solution (pH ~12.4).
Aqueous solution is called limewater; suspension in water is milk of lime.
Reactivity:
Absorbs CO₂ to form calcium carbonate (carbonation):
Ca(OH)2+CO2→CaCO3↓+H2OCa(OH)X2+COX2=>CaCOX3↓+HX2O
Reacts with acids to form salts and water (neutralization):
Ca(OH)2+2 HCl→CaCl2+2 H2OCa(OH)X2+2HCl=>CaClX2+2HX2O
Decomposes at ~580°C to CaO and water vapor.
| Field | Use |
|---|---|
| Construction | Key ingredient in mortar, plaster, and whitewash (binds sand/aggregates). |
| Water Treatment | Adjusts pH, removes impurities (e.g., heavy metals via precipitation). |
| Chemical Industry | Precursor for bleach, caustic soda, and calcium salts (e.g., CaCl₂). |
| Agriculture | Soil amendment (lime) to neutralize acidity and add calcium. |
| Food Industry | Food additive (E526) in pickling, sugar refining, and nixtamalization of corn. |
| Dentistry | Root canal filler (apexification) due to antibacterial properties. |
Strong base: Causes skin/eye burns; releases heat when mixed with water.
Inhalation of dust irritates respiratory tract.
Use protective gear (gloves, goggles) during handling.
Rarely found in nature as the mineral portlandite (e.g., in volcanic or metamorphic rocks).
Primarily synthesized industrially via lime slaking.
Summary: Calcium hydroxide bridges ancient construction (Roman concrete) and modern industry through its versatility as a low-cost alkali. Its dual role—as a structural binder and chemical reagent—stems from its reactivity with CO₂, acids, and metal ions, while its controlled alkalinity makes it vital in environmental and food processes.
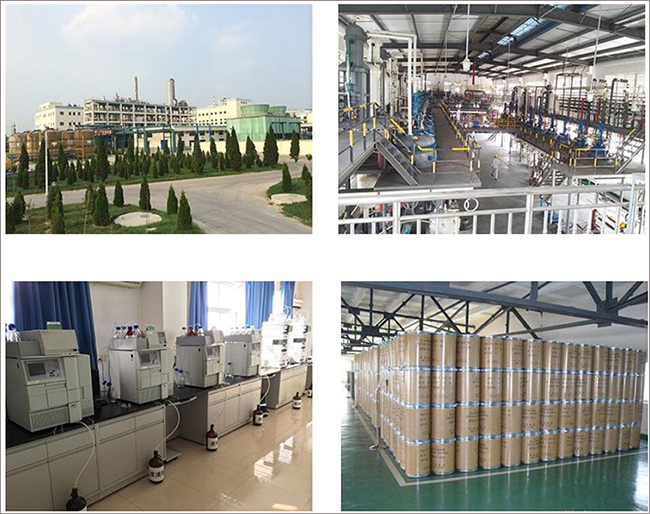
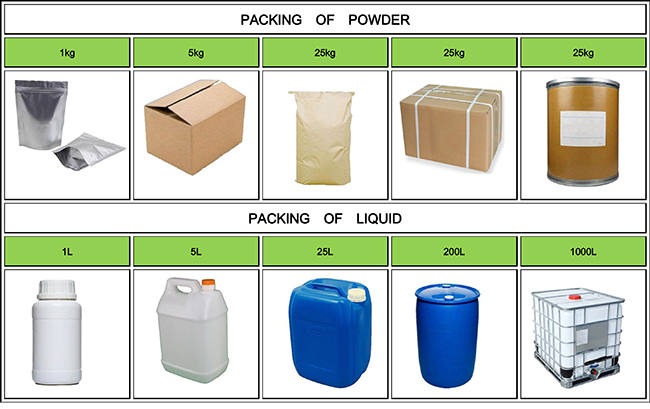



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 
hexanethiol.1主图_20250516.jpg)




