Search

Search









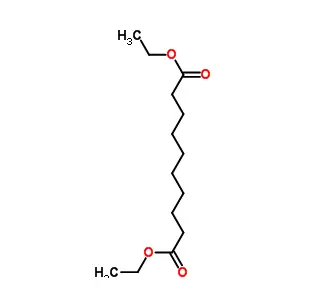
Epilactose is a rare disaccharide and an epimer of lactose. It consists of β-D-galactose linked to D-mannose via a β-1,4-glycosidic bond (unlike lactose, which links galactose to glucose). It is formed through the epimerization of lactose (rearrangement of hydroxyl groups at the C2 position of the glucose unit, converting it to mannose).
Source: Produced via enzymatic or chemical modification of lactose (e.g., using alkali or epimerases).
Function: Acts as a prebiotic, promoting beneficial gut bacteria growth.
Properties: Non-digestible by humans, low-calorie, and heat-stable.
Applications: Used in functional foods, infant formula, and pharmaceuticals for gut health support.
Epilactose is studied for its potential to improve intestinal microbiota and metabolic health.
EPILACTOSE is a rare disaccharide and an epimer of lactose. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Composition:
Epilactose consists of two monosaccharides:
Linkage: A β(1→4) glycosidic bond connects the C1 of galactose to the C4 of mannose.
Systematic Name: β-D-Galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-mannopyranose.
D-Galactose (β-configuration at the anomeric carbon, C1).
D-Mannose (instead of glucose, as in lactose).
Lactose is β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose. In epilactose:
The glucose unit in lactose is replaced by its C2 epimer, mannose (they differ in stereochemistry at the second carbon).
This makes epilactose structurally analogous to lactose but with distinct biochemical properties.
Epilactose is not naturally abundant but can be synthesized via:
Enzymatic Epimerization:
Using enzymes like cellobiose 2-epimerase or lactose epimerase, which catalyze the conversion of lactose to epilactose by epimerizing glucose to mannose.
Chemical Methods:
Alkaline or acidic treatment of lactose under controlled conditions.
Reducing Sugar: The free anomeric carbon (C1) of mannose makes it a reducing sugar.
Low Sweetness: Less sweet than sucrose or lactose.
Prebiotic Potential: May selectively promote beneficial gut bacteria (e.g., Bifidobacteria).
Functional Foods: Used as a prebiotic additive to improve gut health.
Pharmaceuticals: Investigated for anti-inflammatory or anti-cancer properties.
Biotechnology: Serves as a substrate for enzymatic studies or rare sugar production.
Epilactose is found in trace amounts in:
Milk (after heat treatment or enzymatic activity).
Fermented dairy products.
As a "rare sugar," epilactose is gaining interest for its potential health benefits and applications in food science and medicine. Its unique structure and prebiotic properties make it a focus of ongoing research.
Summary: Epilactose is a β(1→4)-linked galactose-mannose disaccharide, distinct from lactose due to the C2 epimerization of glucose to mannose. It is a reducing sugar with emerging roles in nutrition and biotechnology.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية ![Methanesulfonic acid, 1,1,1-trifluoro-, 6-bromo-1,3-dioxo-1H-benz[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl ester CAS 1643932-15-3 Methanesulfonic acid, 1,1,1-trifluoro-, 6-bromo-1,3-dioxo-1H-benz[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl ester CAS 1643932-15-3](/uploads/image/20240726/13/methanesulfonic-acid-111-trifluoro--6-bromo-13-dioxo-1h-benzdeisoquinolin-23h-yl-ester.jpg)