Search

Search











It forms a gel when mixed with sugar and acid, a key functional trait.
Classified as a dietary fiber, it’s indigestible by human enzymes.
Food Industry: Primary use is as a gelling agent in jams, jellies, and marmalades. It also acts as a stabilizer in yogurt, fruit juices, and baked goods, and a thickener for sauces and fillings.
Dietary & Health: Supports digestive health by promoting gut flora balance and aiding regularity. It may help lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels.
Other Applications: Used in pharmaceuticals (e.g., tablet binders) and cosmetics (e.g., skin moisturizers) for its thickening and stabilizing properties.
Items | Specifications | Results |
Identification | 0.76*10-5mol | |
Degree of esterieication | 55~65% | 60% |
Galacturonic acid | ≥74.0% | 86% |
Methoxy Groups | ≥6.7% | 7.0 |
Arsenic | ≤3 | <3 |
Sulfur dioxide | ≤50 | <50 |
Sugars and organic acids | ≤20 | 11 |
Meanthol ethanol and isopropanol | ≤1 | <0.3 |
Loss on drying | ≤10 | 7.9 |
The total aerobic microbial count | ≤1000 | <10 |
The total combined molds and yeasts count | ≤100 | <10 |
Conclusion | The above result complies with the standard. | |
Pectin is a naturally occurring water-soluble polysaccharide that plays a critical structural role in the cell walls and middle lamella of fruits, vegetables, and some plant tissues. It is most abundant in the peels, cores, and pulps of citrus fruits (like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits), apple pomace (the leftover skins and cores from juice production), and berries (such as strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries). Less concentrated sources include carrots, potatoes, and green vegetables, but these are rarely used for commercial extraction due to lower yields. Chemically, pectin is composed of galacturonic acid units linked by glycosidic bonds, with varying degrees of methylation (esterification) that determine its functional properties—high-methoxyl pectin requires sugar and acid to gel, while low-methoxyl pectin can gel with calcium ions, making it suitable for low-sugar products.
Gelling Ability: Its most defining trait is the ability to form a viscous gel when combined with specific triggers (sugar/acid for high-methoxyl, calcium for low-methoxyl). This gelation occurs as pectin molecules bind together, trapping water and creating a semi-solid structure.
Solubility: It dissolves easily in warm water but is insoluble in alcohol, a property used in commercial extraction processes to precipitate and purify pectin from plant materials.
Dietary Fiber Nature: As a soluble fiber, pectin resists digestion by human digestive enzymes. Instead, it passes through the stomach and small intestine intact, reaching the colon where it acts as a prebiotic.
Stability: Pectin remains stable under moderate heat and acid conditions, making it ideal for food processing methods like cooking, pasteurization, and canning.
Jams, Jellies, and Marmalades: The primary use of pectin is to create the characteristic gel texture in these preserves. Without pectin, fruits with low natural pectin content (like strawberries or peaches) would remain runny instead of setting into a spreadable gel. High-methoxyl pectin is preferred here, as it works with the natural sugars and acids in fruit to form a firm gel.
Low-Sugar and Sugar-Free Products: Low-methoxyl pectin is used in diet-friendly jams, jellies, and desserts. It gels with calcium rather than sugar, allowing manufacturers to reduce or eliminate added sugars while maintaining texture.
Dairy Products: It acts as a stabilizer in yogurt, kefir, and cultured creams, preventing separation of whey (the watery layer that forms on top of yogurt) and improving mouthfeel. In ice cream and sorbet, pectin helps control crystal formation, resulting in a smoother texture.
Baked Goods: Added to cakes, cookies, and pastries, pectin enhances moisture retention, extends shelf life, and improves texture. It can also act as a binding agent in fruit fillings, preventing them from oozing out of pastries during baking.
Beverages: Used as a clarifying agent in fruit juices and wines, helping to remove suspended particles and create a clear liquid. It also thickens smoothies, fruit punches, and sports drinks, improving their body and mouthfeel.
Confectionery: Found in gummy candies, fruit chews, and marshmallows, where it acts as a gelling agent to create the chewy, elastic texture. It is often combined with gelatin or agar for optimal consistency.
Digestive Health: As a prebiotic, pectin feeds the "good" bacteria in the gut (such as Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli), promoting a balanced gut microbiome. It also absorbs water in the colon, softening stool and promoting regular bowel movements, which helps prevent constipation. For those with diarrhea, pectin’s water-absorbing properties can help firm stool by binding excess fluid.
Cholesterol Management: Pectin binds to bile acids (which are made from cholesterol) in the intestines, preventing their reabsorption into the bloodstream. The body then uses more cholesterol to produce new bile acids, leading to a reduction in LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels. Studies have shown that regular intake of pectin (especially from citrus fruits) can lower LDL cholesterol by 5-10% over time.
Blood Sugar Regulation: Pectin slows the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine, preventing sharp spikes in blood glucose levels after meals. This is particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Weight Management: Pectin increases feelings of fullness (satiety) by expanding in the stomach, reducing overall calorie intake. It also slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach, helping to curb cravings and overeating.
Detoxification: Pectin can bind to heavy metals (such as lead, mercury, and cadmium) and environmental toxins in the gut, preventing their absorption and facilitating their excretion from the body. This makes it a popular ingredient in detox supplements.
Tablet Binders and Disintegrants: In tablet manufacturing, pectin acts as a binder, holding active ingredients together to form a cohesive tablet. It also functions as a disintegrant, helping the tablet break down quickly in the stomach to release the medication.
Drug Delivery Systems: Pectin-based hydrogels are used in controlled-release drug formulations. These gels can be designed to release medications slowly over time (e.g., in the colon or small intestine), improving the effectiveness of the drug and reducing side effects.
Wound Care: Pectin-based dressings are used for chronic wounds (such as diabetic ulcers) due to their ability to absorb exudate (wound fluid), maintain a moist healing environment, and promote tissue regeneration. The gel-forming property of pectin helps keep the dressing in place while protecting the wound from infection.
Antacid and Digestive Aids: Pectin is added to antacids and digestive supplements to soothe the stomach lining, reduce acid reflux, and support healthy digestion. Its ability to absorb excess stomach acid and form a protective gel layer makes it effective for relieving heartburn and indigestion.
Skin Care: Found in lotions, creams, masks, and serums, pectin acts as a thickener, giving products a smooth, luxurious texture. It also helps retain moisture in the skin by forming a hydrating film, making it suitable for dry and sensitive skin types. Some formulations use pectin as a natural alternative to synthetic thickeners like carbomers.
Hair Care: Added to shampoos, conditioners, and hair masks, pectin helps detangle hair, reduce frizz, and improve manageability. It coats the hair shaft, locking in moisture and adding shine without weighing hair down.
Oral Care: Used in toothpaste and mouthwash, pectin acts as a stabilizer and thickener, improving the texture and consistency of the product. It can also help soothe irritated gums and promote oral health by supporting beneficial bacteria in the mouth.
Textile Industry: Pectin is used as a sizing agent for cotton and other natural fibers. It coats the fibers, improving their strength and smoothness, which makes them easier to weave into fabric. After weaving, the pectin is washed away, leaving the fabric soft and breathable.
Paper Industry: Added to paper pulp, pectin acts as a binder, improving the strength and durability of paper. It also helps in the retention of fine fibers and fillers, reducing waste during the papermaking process.
Biodegradable Packaging: Pectin is being explored as a raw material for biodegradable packaging materials. When combined with other natural polymers (like starch or chitosan), it can form edible or compostable films that replace plastic packaging, reducing environmental waste.
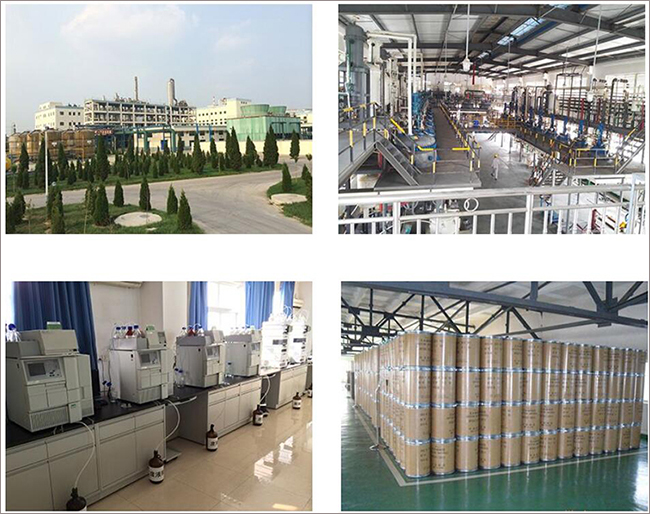




Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية