Search

Search











o-Anisic acid (2-methoxybenzoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula C₈H₈O₃. It appears as white crystals with a sweet, hay-like aroma. Primarily used as a fragrance ingredient and fixative in perfumes and cosmetics, it helps stabilize scents. It also serves as a key chemical intermediate in synthesizing pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. Its structure features a methoxy group adjacent to the carboxylic acid on the benzene ring, defining its unique properties and applications in industry.
o-Anisic acid, also known by its systematic name 2-methoxybenzoic acid, is an organic compound. It is one of the three isomers of anisic acid, distinguished by the position of the methoxy group (-OCH₃) relative to the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) on the benzene ring. The prefix "o-" (for ortho-) specifies that the methoxy group is attached to the carbon atom adjacent to the one bearing the carboxylic acid group.
Its chemical formula is C₈H₈O₃.
It occurs naturally in small amounts in various plants but is typically produced synthetically for commercial use.
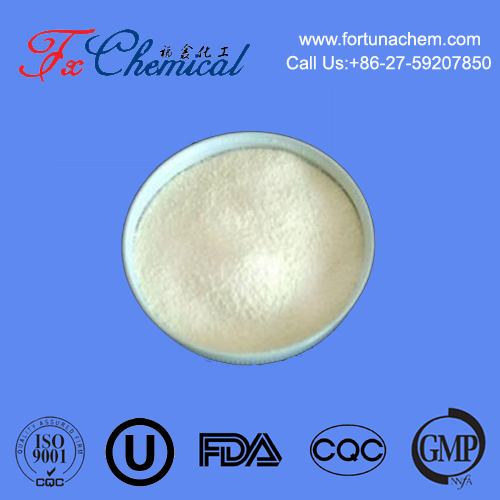
Appearance: It typically presents as white to off-white crystalline needles or a powder.
Melting Point: It has a relatively low melting point for a solid organic acid, around 101-103 °C.
Odor: It has a sweet, creamy, and slightly phenolic odor, often described as reminiscent of hay or honey. This makes it valuable in fragrance applications.
Solubility: It is sparingly soluble in cold water but more soluble in hot water. It dissolves readily in organic solvents like ethanol, ether, and chloroform.
o-Anisic acid's applications are primarily driven by its pleasant fragrance and its function as a versatile chemical building block.
This is one of its most significant uses.
Perfumery: Its sweet, creamy, and long-lasting odor makes it a useful ingredient in fragrance compositions. It acts as a fixative, helping to slow the evaporation of more volatile scent components and stabilizes the overall aroma profile. It is found in perfumes, soaps, detergents, and cosmetics.
Flavoring Agent: It is used in small quantities to impart sweet, creamy nuances to food flavors, though this use is less common than its application in fragrances.
Intermediate: o-Anisic acid serves as a key starting material or chemical intermediate in the synthesis of more complex pharmaceutical compounds.
API Synthesis: It is used in the production of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), including some vasodilators (medications that widen blood vessels) and other drugs where the ortho-methoxybenzoic structure is a key pharmacophore.
Building Block: The molecule contains two functional groups (carboxylic acid and ether) that can be selectively modified. This makes it a versatile synthon (synthetic building block) for chemists.
Ligand Precursor: It can be used to derive ligands for metal catalysts used in various chemical reactions.
Antimicrobial Properties: Like many organic acids, o-anisic acid and its derivatives (particularly its esters) exhibit antimicrobial and preservative qualities. It can be used to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, making it useful in certain niche preservation applications, though it is not as common a preservative as parabens or benzoic acid.
Toxicity: o-Anisic acid is generally considered to have low acute toxicity. However, like many organic acids, it can be irritating.
Irritant: It may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Dust inhalation should be avoided.
Handling: Standard laboratory precautions should be followed when handling this chemical, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses.
It's helpful to distinguish it from its isomers:
| Isomer | Systematic Name | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| o-Anisic Acid | 2-methoxybenzoic acid | Methoxy group is ortho (adjacent) to the acid group. |
| m-Anisic Acid | 3-methoxybenzoic acid | Methoxy group is meta (one carbon away) to the acid group. |
| p-Anisic Acid | 4-methoxybenzoic acid | Methoxy group is para (opposite) to the acid group. |
The ortho position in o-anisic acid creates unique steric and electronic effects that influence its physical properties (like its lower melting point compared to the meta and para isomers) and its chemical reactivity.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| What it is | An organic compound, specifically the ortho isomer of methoxybenzoic acid. |
| Chemical Formula | C₈H₈O₃ |
| Key Property | A white crystalline solid with a sweet, creamy, hay-like odor. |
| Primary Uses | 1. Fragrance ingredient and fixative in perfumes and cosmetics. 2. Chemical intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis. 3. Building block in organic chemistry. |
| Context | A specialty chemical used primarily in the fragrance, flavor, and pharmaceutical industries. |
In essence, o-anisic acid is a versatile aromatic acid valued for its sensory properties and its utility as a foundational molecule for creating more complex chemical structures.

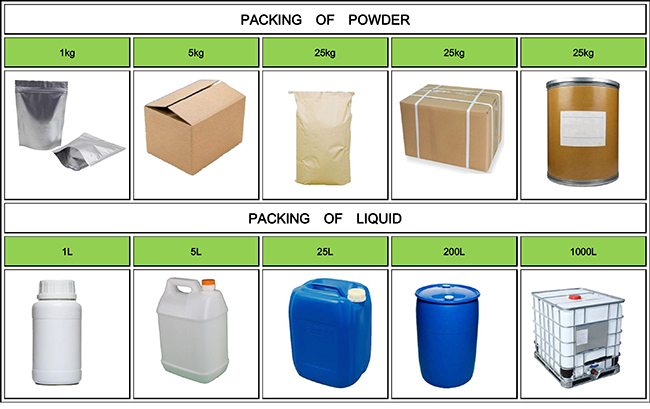


Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 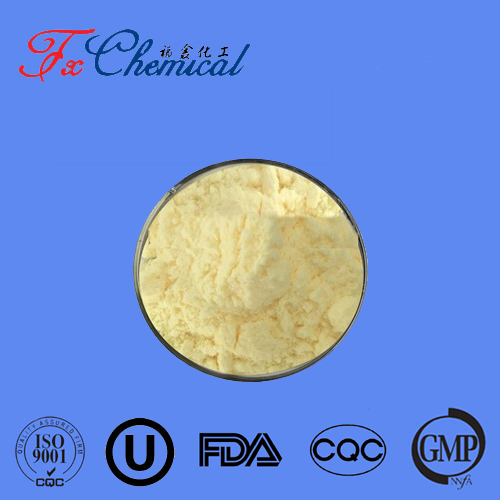
主图.jpg)



