Search

Search











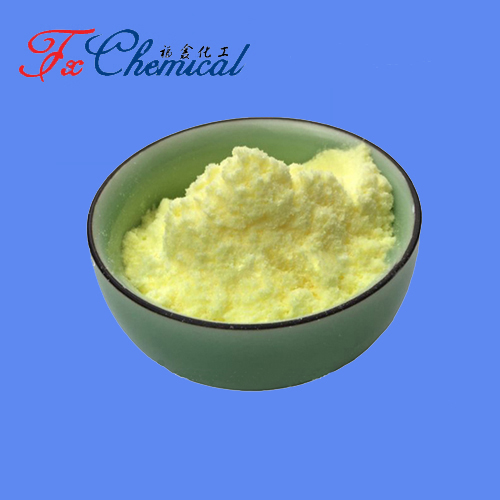
Rutin (C27H30O16 (C27H30O16C27H30O16)) is a flavonoid glycoside where quercetin binds rutinose (rhamnose + glucose). It’s a yellow, water-insoluble solid from buckwheat/citrus. Key actions:
Antioxidant: Neutralizes free radicals via catechol groups.
Capillary protector: Reduces bruising/edema by strengthening blood vessels.
Anti-inflammatory: Inhibits enzymes like cyclooxygenase.
Used in supplements for vascular health, pharmaceuticals (e.g., venous disorders), and as a natural stabilizer. Poor oral bioavailability is improved by gut microbiota converting it to active quercetin.
Rutin (also called rutoside or *quercetin-3-O-rutinoside*) is a bioactive flavonoid glycoside found in plants like buckwheat, citrus fruits, and asparagus. Here's its chemical breakdown:
Core Structure:
Composed of the flavonol quercetin (aglycone) linked to the disaccharide rutinose (α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranose).
Glycosidic Bond: Quercetin’s C3-OH group binds to rutinose’s glucose unit.
Formula:
C27H30O16
Molar Mass: 610.52 g/mol.
Properties:
Yellow crystalline solid.
Poor water solubility (soluble in alkaline solutions/alcohols).
Antioxidant: Scavenges free radicals via catechol group in quercetin.
Biological Roles:
Vasoprotective: Strengthens capillaries and reduces permeability.
Anti-inflammatory & Antithrombotic: Inhibits platelet aggregation.
Metal Chelator: Binds iron/copper, reducing oxidative stress.
Natural Sources:
Buckwheat, apples, citrus rind, elderflower, green tea.
Uses:
Dietary supplements (vascular health).
Pharmaceutical ingredient (e.g., for hemorrhoids, venous insufficiency).
Natural antioxidant in cosmetics/food.
CAS Number: 153-18-4
Rutin’s dual sugar moiety enhances bioavailability compared to quercetin. Its catechol group (ring B) and conjugated system enable potent redox activity.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية