Search

Search











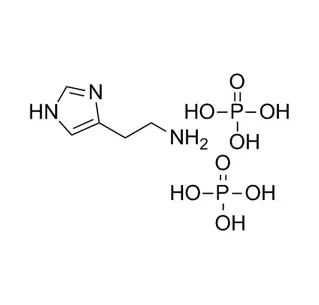
Fmoc-O-tert-butyl-D-serine is a chemically modified, non-natural amino acid used primarily as a building block in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS).
Key Features:
Fmoc group: Protects the amine, allowing for sequential peptide chain elongation.
O-tert-butyl group: Protects the reactive serine side-chain hydroxyl.
D-configuration: The mirror-image form of natural serine.
Uses: It is employed to incorporate D-serine into synthetic peptides. This enhances peptide stability against enzymatic degradation in drug discovery and creates specific 3D structures in research peptides for biochemistry and material science.
Fmoc-O-tert-butyl-D-serine is a protected, non-natural amino acid derivative used almost exclusively as a building block in synthetic organic chemistry, specifically in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS).
Its name systematically describes its structure:
Fmoc (9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl): A protecting group for the amine (-NH₂) function of the amino acid. It is stable under the conditions used to assemble the peptide chain but can be removed gently with a base (like piperidine) without affecting other parts of the growing molecule.
D-Serine: This indicates the mirror-image (unnatural) form of the amino acid serine. Naturally occurring serine is in the L-configuration. Using the D-form introduces specific structural properties into a synthetic peptide, such as resistance to enzymatic degradation or the ability to form particular 3D structures.
O-tert-butyl: This is a protecting group for the hydroxyl (-OH) side chain of serine. The side chain of serine is reactive and would interfere with the peptide bond-forming reactions. The bulky, hydrophobic tert-butyl group blocks this reactivity. It is stable under the conditions used for Fmoc removal and peptide coupling but can be removed later with a strong acid (like trifluoroacetic acid, TFA).
In essence, it is a chemically modified, "ready-to-use" version of D-serine designed for controlled assembly into custom peptide chains.
This is its exclusive and critical application. SPPS is the standard method for creating custom peptides in the lab, from small fragments to complex proteins.
Building Block: It serves as one of the specific "bricks" to be incorporated at a defined position in the peptide sequence.
Protection Strategy: Its design follows the standard Fmoc/*t*-Bu strategy:
The Fmoc group allows for selective, step-by-step chain elongation.
The O-tert-butyl group ensures the serine side chain remains inert during synthesis.
To Incorporate D-Serine: The key reason. Researchers use it to create peptides that:
Mimic natural peptides but with enhanced stability against proteases (enzymes that break down peptides in the body), which is crucial for potential therapeutic drugs.
Study the effects of chirality on peptide structure and function.
Create "mirror-image" peptides (all-D peptides) for drug discovery or structural biology.
To Ensure Clean Synthesis: The protecting groups prevent unwanted side reactions, leading to higher purity and yield of the final target peptide.
Chemical Biology & Drug Discovery: Used to synthesize peptide-based inhibitors, probes, or potential drug candidates where incorporating a D-amino acid is beneficial for stability, binding, or activity.
Material Science: Peptides containing D-amino acids can self-assemble into unique nanostructures (like hydrogels) with specific mechanical or biological properties. This compound is a key reagent to make such peptides.
Research into Peptide Structure & Function: To investigate how the chirality of a single residue affects the folding, stability, and activity of an entire peptide or protein domain.
Peptide Chemists in academia and pharmaceutical/biotech R&D.
Chemical Biologists studying protein-protein interactions.
Researchers in medicinal chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science.
Form: Typically a white to off-white crystalline powder.
Storage: Stored refrigerated or frozen, desiccated, and protected from light to prevent degradation.
Solubility: Soluble in polar aprotic solvents commonly used in SPPS, such as Dimethylformamide (DMF) or N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP).
Cost: Significantly more expensive than its natural L-serine counterpart due to the chirality-specific synthesis and purification required.
Fmoc-O-tert-butyl-D-serine is a specialized, protected amino acid building block for synthetic peptide chemistry. Its sole purpose is to enable the controlled, automated incorporation of D-serine into custom-designed peptide chains. This allows scientists to create peptides with unnatural backbones for applications in drug development, biochemical research, and advanced materials, where properties like protease resistance and unique 3D structure are desired. It is a fundamental tool in the toolkit of modern peptide science.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية