Search

Search











DL-3-Aminoisobutyric acid (DL-3-AIB) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid (C₄H₉NO₂) with a branched-chain structure, featuring an amino group (-NH₂) at position 3 and a methyl group (-CH₃) at position 2. It exists as a racemic mix (D- and L-enantiomers) and is produced during thymine and valine catabolism. Functionally, it acts as a signaling molecule linked to metabolic benefits, such as enhancing insulin sensitivity, promoting mitochondrial biogenesis, and mimicking exercise-induced effects (e.g., fat oxidation). Research explores its role in obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular health. Water-soluble and chiral, it is also used in peptide synthesis. Elevated levels may correlate with metabolic disorders or genetic conditions.
DL-3-Aminoisobutyric acid (DL-3-AIB), also known as β-aminoisobutyric acid (BAIBA), is a non-proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula C₄H₉NO₂. It exists as a racemic mixture (DL form), meaning it contains both D- and L-enantiomers in equal proportions. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Core Structure: A branched-chain amino acid derived from isobutyric acid (2-methylpropanoic acid).
Functional Groups:
A carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at position 1.
A methyl group (-CH₃) at position 2.
An amino group (-NH₂) at position 3.
IUPAC Name: 3-Amino-2-methylpropanoic acid.
Stereochemistry: The "DL" prefix indicates a racemic mix of the D (right-handed) and L (left-handed) enantiomers.
Metabolism:
Produced during the catabolism of thymine (a pyrimidine base in DNA) and the branched-chain amino acid valine.
Acts as a metabolite in the urea cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Signaling Molecule:
Linked to enhanced insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial biogenesis.
Associated with exercise-induced benefits, such as improved metabolic health (e.g., "exercise mimetic" properties).
Tissue Distribution:
Found in humans, other mammals, and microorganisms.
Elevated levels may correlate with metabolic disorders or genetic conditions.
Research: Studied for its potential role in obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular health.
Biotechnology: Used in peptide synthesis and as a chiral building block.
Chirality: The D- and L-forms may exhibit distinct biological activities.
Solubility: Polar due to amino and carboxylic acid groups, soluble in water.
In summary, DL-3-Aminoisobutyric acid is a metabolically active compound with emerging roles in metabolic regulation and disease research. Its racemic nature and branched structure make it a unique subject in biochemistry and pharmacology.
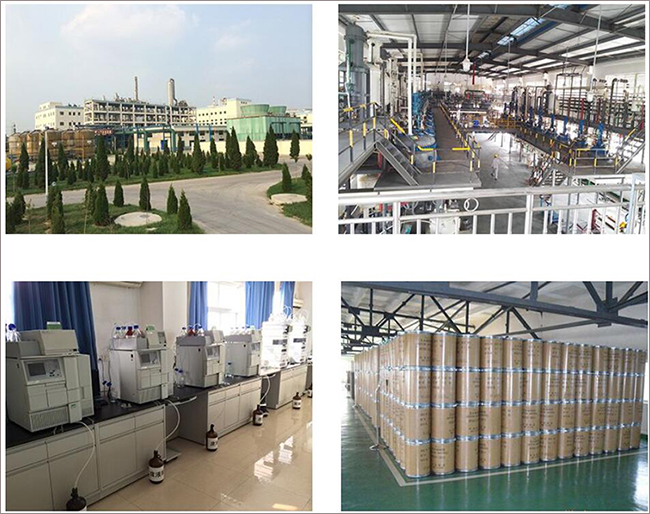


Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 





