
Search

Search











16-Dehydro pregnenolone acetate is used as an intermediate for cortisone acetate, hydrocortisone and 16-Dehydro pregnenolone acetate caproate.16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate is a synthetic steroid compound, not a final medication itself. It serves as a crucial key intermediate in the industrial synthesis of other, more complex steroids.
Its primary importance lies in the production of a class of drugs called corticosteroids (powerful anti-inflammatory agents) and progestogens (hormones involved in the menstrual cycle and pregnancy). It is the chemical starting point or a "building block" for manufacturing steroids like cortisone, hydrocortisone, and betamethasone.
In short, it's a foundational chemical in pharmaceutical manufacturing to create essential steroid hormones.
| Product Name | 16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate |
| Apperance | White crystalline powder |
| EINECS | 213-558-7 |
| MF | C23H32O3 |
| MW | 356.5 |
| Assay | ≥98.0% |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 979-02-2 |
| Appearance: | White crystalline powder |
| Purity: | 98.0%min |
| Package details: | 1kg/bag;20kg/drum |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate (16-DPA) is a critically important synthetic steroid intermediate. It is not a drug or medication itself but a key starting material, or "building block," used in the industrial-scale pharmaceutical synthesis of a wide range of medically essential steroid hormones, particularly corticosteroids and progestogens.
Its significance lies in its unique molecular structure, which provides an ideal foundation for chemical modifications that allow efficient production of complex steroid molecules that would otherwise be difficult and expensive to obtain.
To understand its role, it helps to break down its name and structure:
Pregnenolone Backbone: It is derived from pregnenolone, a natural prohormone produced in the body from cholesterol. This means it has the fundamental four-ring carbon skeleton common to all steroid hormones.
Acetate Group: The "acetate" refers to an acetyl group attached to the oxygen at the 3-position of the steroid. This group protects the molecule during chemical reactions, making it more stable and easier to work with.
The Key Feature - 16-Dehydro: The most crucial part of its name is "16-Dehydro." This indicates a double bond between carbon atoms 16 and 17 in the steroid's D-ring. This double bond is the key reactive site that unlocks its utility. It makes the molecule highly receptive to chemical reactions that are fundamental to building more complex structures.
The importance of 16-DPA exploded in the mid-20th century with the discovery of cortisone's powerful anti-inflammatory effects. There was an urgent need to produce large quantities of cortisone and related corticosteroids, but isolating them from natural sources was incredibly inefficient.
16-DPA, which could be semi-synthesized in large quantities from readily available plant sterols like diosgenin (found in Mexican yams), became the solution. It served as the launchpad for the Marker Degradation and Partial Synthesis pathways, which revolutionized steroid manufacturing.
16-DPA's structure is strategically modified to produce various classes of steroid drugs:
Corticosteroids (Anti-inflammatories): This is its most significant application. The 16-Double bond allows for a crucial microbial step using specific bacteria or fungi (e.g., Rhizopus species) that easily add oxygen atoms to the 11-position of the steroid ring. An oxygen at C-11 is a mandatory structural feature for potent glucocorticoid activity (anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects). From 16-DPA, manufacturers can efficiently produce:
Cortisone and Hydrocortisone
Prednisone
More potent steroids like Betamethasone and Dexamethasone.
Progestogens (Sex Hormones): 16-DPA is also a key intermediate in synthesizing various progestins (synthetic progesterone). It can be chemically converted into hormones like:
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (used in hormonal birth control and hormone therapy).
In essence, 16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate is a workhorse of steroid chemistry. While unknown to patients, it is a foundational pillar of the modern pharmaceutical industry. Its cleverly designed structure, featuring the reactive 16-double bond, provides an efficient and cost-effective pathway for the large-scale synthesis of life-saving anti-inflammatory steroids and essential sex hormones, making it one of the most important intermediates in the history of steroid drug production.
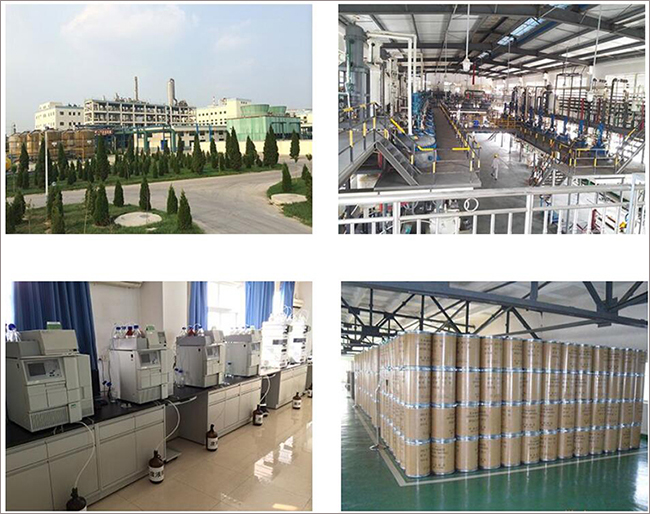





Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 

![3-Azabicyclo[3.3.0]Octane Hydrochloride CAS 112626-50-3 3-Azabicyclo[3.3.0]Octane Hydrochloride CAS 112626-50-3](/uploads/image/20220323/14/chemical-price.jpg)



