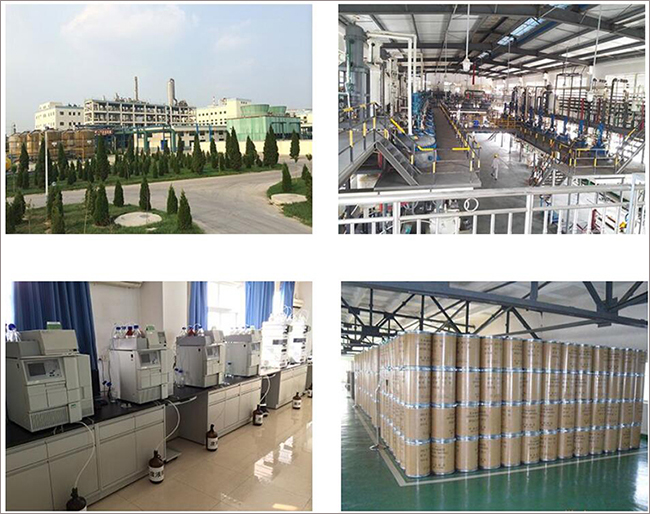
Guaranteed purity
High quality & competitive price
Quality control
Fast feedback
Prompt shipment

Search

Search











D-Aspartic Acid (D-Asp) is the D-stereoisomer of the amino acid aspartic acid. Its core structure consists of a four-carbon chain with:
An amino group (-NH₂) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the alpha carbon, defining it as an amino acid.
A second carboxyl group on the side chain, making it a dicarboxylic acid.
The defining D-configuration refers to the specific, non-superimposable mirror-image spatial arrangement of these groups around the chiral alpha carbon, opposite to the common, proteinogenic L-Aspartic Acid.
Unlike its L-form, D-Asp is not incorporated into proteins during ribosomal synthesis. Instead, it functions as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in the central nervous system and plays a role in the endocrine system, notably in the regulation of hormone release in the pituitary gland and testes. It is found in various tissues and is synthesized from L-Aspartic acid by the enzyme aspartate racemase.
Items | Specifications | Results |
Appearance | Complies | |
State of solution | ≥98.0% | 98.6% |
Specific Rotation | -24.0°~ -26.0° | -24.5° |
Chloride(Cl) | ≤0.02% | <0.02% |
Ammonium(NH4) | ≤0.02% | <0.02% |
Sulfate(SO4) | ≤0.02% | <0.02% |
Iron(Fe) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
Heavy metals(Pb) | ≤10ppm | <10ppm |
Arsenic(As2O3) | ≤1ppm | <1ppm |
Loss on drying | ≤0.20% | 0.13% |
Residue on ignition | ≤0.10% | 0.06% |
PH | 2.5~3.5 | 3.0 |
Assay | 99.0~101.0% | 99.5% |
Conclusion | The product by inspection accords with the standard of Enterprise Internal. | |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 1783-96-6 |
| Appearance: | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Purity: | 99%min |
| Package details: | 25kg/drum |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
D-Aspartic Acid (D-Asp) is one of the two stereoisomers of the amino acid aspartic acid. Its molecular formula is C₄H₇NO₄.
The "D-" designation is its most critical chemical feature. Like most amino acids, aspartic acid has a chiral center at its alpha carbon (the central carbon atom). This means it exists in two non-superimposable mirror-image forms: L-Aspartic Acid and D-Aspartic Acid.
L-Aspartic Acid: This is the form incorporated into proteins during ribosomal synthesis. It is one of the 20 standard proteinogenic amino acids and plays key roles in metabolism, such as the urea cycle and gluconeogenesis.
D-Aspartic Acid: This is the enantiomer (mirror image) of the L-form. Its spatial configuration is defined by its specific three-dimensional arrangement around the chiral alpha carbon. In the Fischer projection, the D-isomer has the amino group (-NH₂) on the right side.
Its core structure consists of:
An amino group (-NH₂) attached to the chiral alpha carbon.
A carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the alpha carbon.
A side chain composed of a second carboxyl group (-COOH), which classifies it as a dicarboxylic, acidic amino acid.
Unlike L-aspartic acid, D-Asp is not produced by the ribosome. Its presence in biological systems results from a process called racemization. The enzyme aspartate racemase catalyzes the conversion of L-Aspartic Acid to D-Aspartic Acid. It is found in various tissues across the body, with notably high concentrations in the brain, pituitary gland, pineal gland, and testes.
D-Aspartic Acid is classified as a non-proteinogenic amino acid, but it is far from biologically inert. It acts as a novel neurotransmitter and neuromodulator and plays crucial roles in the endocrine system:
Neurotransmission in the Central Nervous System: D-Asp acts as a signaling molecule in the brain. It binds to the NMDA (N-Methyl-D-Aspartate) receptor, the very receptor named for its selective activation by this isomer. By modulating this receptor, D-Asp can influence synaptic plasticity, which is fundamental to learning and memory.
Endocrine Regulation (Hormone Release): This is one of its most significant roles.
In the Pituitary Gland: D-Asp stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), growth hormone (GH), and prolactin.
In the Testes: It accumulates in the testes' Leydig cells and promotes the synthesis and release of testosterone. It does this by upregulating the expression of the steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein and the enzyme cytochrome P450scc, which are critical for testosterone production. This function has made it a popular, though debated, dietary supplement for athletic performance and fertility.
Role in Development: Its levels are high during embryonic development, suggesting a role in the formation of the nervous system.
In essence, D-Aspartic Acid is the non-proteinogenic, D-enantiomer of aspartic acid. While it shares the same molecular formula as its L-form, its distinct three-dimensional structure allows it to function not as a building block for proteins, but as a specialized signaling molecule. It is an endogenous compound in humans and other animals, serving critical roles as a neuromodulator in the brain and a key regulator of hormone production in the endocrine system, particularly influencing reproductive hormones and growth.




Guaranteed purity
High quality & competitive price
Quality control
Fast feedback
Prompt shipment

Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 


-Asparagine_monohydrate主图.jpg)


