Search

Search











J acid (6-Amino-1-naphthol-3-sulfonic acid) is a key industrial chemical used primarily as a building block for synthesizing azo dyes and pigments. Its molecular structure features both an amino group and a hydroxyl group, allowing it to couple with other compounds to form brightly colored dyes. These dyes are widely used for coloring cotton textiles and paper. The sulfonic acid group makes J acid water-soluble and helps the final dyes bind effectively to fabrics. It is not a dye itself but an essential intermediate for producing vibrant, durable shades like yellows, oranges, and reds.
Items | Specifications | Results |
Appearance | Conform | |
Content(dry) | ≥90.00% | 90.07% |
Purity(HPLC) | ≥97.00% | 97.01% |
Γ Acid | ≤1.00% | 0.99% |
Double-J Acid | ≤0.20% | 0.18% |
Thealkali insoluble | ≤0.50% | 0.08% |
Moisture | ≤1.00% | 0.98% |
Conclusion | The product Complies to standard. | |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 87-02-5 |
| Appearance: | Grey to light brown powder |
| Purity: | 90%min |
| Package details: | 25kg/drum |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
J acid is the common name for 6-Amino-1-naphthol-3-sulfonic acid. It is an important intermediate (a building block) in the chemical industry, primarily used for the synthesis of azo dyes and pigments.
Its value lies in its molecular structure, which contains two different reactive sites that allow it to couple with other compounds to form brightly colored dyes.
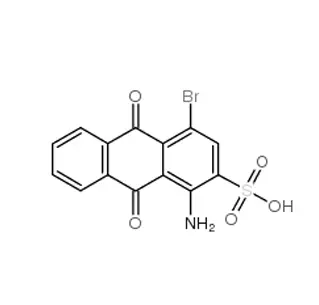
Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₉NO₄S
IUPAC Name: 6-Amino-1-naphthol-3-sulfonic acid
Molecular Structure:
It is based on a naphthalene ring system.
It has three key functional groups attached to it:
An amino group (-NH₂) at the 6-position.
A hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 1-position.
A sulfonic acid group (-SO₃H) at the 3-position.
Appearance: Typically a gray to off-white powder.
Solubility: It is soluble in water, largely due to the presence of the sulfonic acid group, which makes the molecule hydrophilic.
J acid is not a dye itself. Instead, it is a coupling component (or intermediate) in the production of azo dyes, which are the largest and most important class of synthetic dyes.
The Azo Coupling Reaction: This is a reaction between a diazonium salt (an electrophile) and a coupling component (a nucleophile, like J acid).
J Acid's Reactive Sites: J acid has two main reactive sites where this coupling can occur:
The ortho position to the hydroxyl group (most common).
The ortho position to the amino group.
This ability to couple at specific positions allows chemists to create dye molecules with precise structures and properties.
When incorporated into a dye molecule, J acid imparts several valuable properties:
Bright Colors: Dyes made with J acid often produce bright shades of yellow, orange, and red.
Substantivity for Cotton: The sulfonic acid group(s) in the final dye molecule make it water-soluble and able to bind effectively to cellulose fibers like cotton, making it very useful for direct dyes and reactive dyes.
Good Lightfastness: Dyes derived from J acid generally have reasonable resistance to fading when exposed to sunlight.
J acid is exclusively used in the synthesis of more complex chemicals. Its main applications are:
Textile Dyes: It is a key intermediate for dyes used on cotton, silk, and wool.
Paper Dyes: Used in coloring paper.
Organic Pigments: Some J acid derivatives are used as pigments for inks and plastics.
A classic and specific example is the dye "Orange II", which is made by coupling diazotized sulfanilic acid with 2-naphthol. While Orange II doesn't use J acid itself, more complex and lightfast dyes are created using J acid as the coupling component.
Production: The synthesis of J acid from naphthalene is a multi-step process involving sulfonation, nitration, reduction, and hydrolysis.
Environmental Impact: Like many chemical manufacturing processes, the production of J acid and related dyes can generate hazardous waste if not managed properly. Modern facilities have stringent controls to mitigate this.
In essence, J acid (6-Amino-1-naphthol-3-sulfonic acid) is a crucial building block in synthetic dye chemistry. Its well-defined structure with amino, hydroxyl, and sulfonic acid groups allows it to act as a versatile coupling component, enabling the production of a wide range of bright, water-soluble azo dyes used predominantly in the textile industry.




Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية