Search

Search

indole-3-carboxylate主图.jpg)




indole-3-carboxylate主图.jpg)




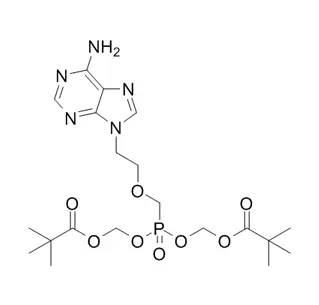
Ethyl 6-bromo-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-[(phenylsulfanyl)methyl]-1H-indole-3-carboxylate is a complex synthetic organic compound built around an indole core. It features multiple functional groups: a bromine atom and a phenol (–OH) on the aromatic ring, a thioether (–S–CH₂–C₆H₅), and an ester (–COOEt). This specific structure is not a final product but is designed as a key intermediate in advanced organic synthesis, particularly in medicinal chemistry for constructing potential drug candidates, such as kinase inhibitors or other biologically active molecules.
Items | Specifications | Results |
Appearance | Off-white to light brown powder | Light brown powder |
Loss on drying
| ≤0.5% | 0.17% |
Residue on ignition | ≤1.0% | 0.18% |
Purity | ≥98.0% | 98.5% |
Related substances | Single impurity NMT1.0% | 0.68% |
Total impurity NMT2.0% | 1.5% | |
Conclusion | Complies with In-house standard. | |
Attention | For Laboratory use only , not for drug and other uses. | |
Here is a detailed explanation of Ethyl 6-bromo-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-[(phenylsulfanyl)methyl]-1H-indole-3-carboxylate.
This is a complex organic molecule, and its systematic name describes its structure piece-by-piece:
Ethyl ... carboxylate: This indicates an ester functional group (-COOCH₂CH₃) attached to the core structure. This makes the molecule relatively lipophilic (fat-soluble).
6-Bromo: A bromine atom (Br) is attached to carbon #6 on the indole ring.
5-Hydroxy: A hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to carbon #5. This group can act as a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor.
1-Methyl: A methyl group (-CH₃) is attached to the nitrogen atom (N) of the indole ring. This "protects" the nitrogen and alters its electronic properties.
2-[(Phenylsulfanyl)methyl]: A thiobenzyl ether group (-CH₂-S-C₆H₅) is attached to carbon #2 of the indole ring. The sulfur atom provides potential for further oxidation or metal coordination.
Indole: The core of the molecule is an indole ring system—a fundamental structure in organic chemistry consisting of a benzene ring fused to a pyrrole ring. Indoles are found in many natural products (e.g., tryptophan, serotonin) and pharmaceuticals.
Molecular Weight: Relatively high (~434 g/mol), typical for a synthetic intermediate.
Solubility: Likely soluble in organic solvents like dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and dimethylformamide (DMF) due to its lipophilic ester and aromatic groups. The phenolic -OH group may grant slight solubility in basic aqueous solutions.
Reactivity: The molecule contains multiple sites for further chemical manipulation:
The bromine atom is an excellent handle for metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions (e.g., Suzuki, Heck reactions) to attach more complex groups.
The phenolic -OH group can be alkylated, acylated, or used to form ethers.
The ester can be hydrolyzed to a carboxylic acid or reduced to an alcohol.
The sulfide (thioether) can be oxidized to a sulfoxide or sulfone.
This compound is not a naturally occurring substance and is not a final product like a drug or material.
It is a Synthetic Intermediate: This molecule is almost exclusively a key building block synthesized in a laboratory for use in organic and medicinal chemistry research.
Purpose: Its complex, multi-functional structure is carefully constructed to serve as a precursor for the synthesis of more elaborate target molecules. A chemist would use its reactive sites (Br, OH) to build a larger, more complex structure around the indole core.
Given its structure, it is designed for advanced synthetic applications, likely in:
Medicinal Chemistry Research: The indole core is a "privileged scaffold" in drug discovery. This specific molecule could be used to synthesize novel potential pharmaceuticals targeting a wide range of diseases, particularly in:
Oncology: Kinase inhibitors or apoptosis inducers.
Neurology: Serotonin receptor modulators.
Materials Science: As a building block for creating organic ligands that could coordinate with metals to form catalysts or functional materials.
Chemical Biology: As a probe to study biological systems or enzyme mechanisms.
In essence, Ethyl 6-bromo-5-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-[(phenylsulfanyl)methyl]-1H-indole-3-carboxylate is a sophisticated, multi-functional synthetic intermediate. Its value lies not in what it is, but in what it can become. A chemist designed it with specific reactive handles (Br, OH, ester, sulfide) to allow for systematic and precise chemical transformations en route to creating a target molecule for research, most likely in the field of drug discovery.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية