Search

Search










L-Threonine is one of the essential amino acids in the human body, which can be used to improve nutrition and improve physical fitness.
L-Threonine is an essential amino acid that helps the body maintain protein balance. It plays a role in the formation of collagen and elastin. When L-Threonine is combined with aspartic acid and methionine, it can resist fatty liver. L-Threonine is found in the heart, central nervous system, and skeletal muscle, preventing the accumulation of fat in the liver. It boosts the production of antibodies to strengthen the immune system. L-Threonine is an important nutritional fortifier that can fortify cereals, pastries, dairy products, and tryptophan has the same effect of restoring human fatigue and promoting growth and development. In medicine, because the structure of L-Threonine contains hydroxyl groups, it has a water-holding effect on human skin, combines with oligosaccharide chains, plays an important role in protecting cell membranes, and can promote phospholipid synthesis and fatty acid oxidation in the body.
| Items | Specifications | Results |
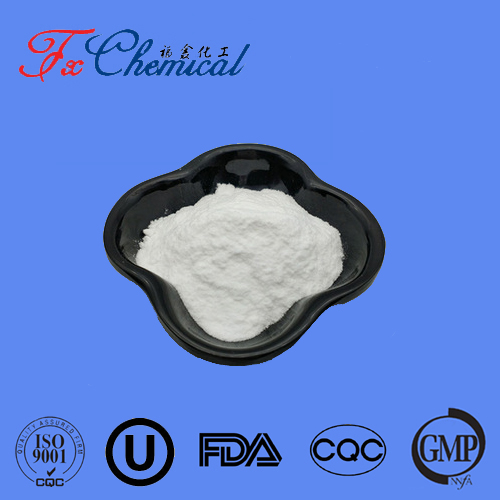
| Appearance | White crystalline powder | conforms |
| Assay | 98.5%min | 99.12% |
| Product parameters | |
| Cas number: | 72-19-5 |
| Appearance: | White crystalline powder |
| Purity: | 98.5%min |
| Package details: | 25kg/drum; 25kg/bag |
| Brand: | Fortunachem |
L-Threonine is one of the twenty standard amino acids that are used as building blocks by cells to synthesize proteins. It is classified as an essential amino acid, which means the human body cannot synthesize it on its own. Therefore, it must be obtained exclusively from the diet.
The "L-" prefix refers to its specific three-dimensional molecular shape (an isomer), which is the form utilized by all living organisms for protein synthesis.
As a crucial component of proteins, L-Threonine serves several vital functions in the body:
Protein Synthesis: It is a fundamental building block for making proteins throughout the body, including muscles, organs, and enzymes.
Structural Proteins: It is a major component of structural proteins that are critical for tissue strength and integrity. Most notably:
Collagen: A primary protein in skin, connective tissues, and bones.
Elastin: Allows tissues like skin and blood vessels to resume their shape after stretching.
Tooth Enamel: Helps form the strong outer layer of teeth.
Mucin Production: Threonine is a key ingredient in the production of mucin, a glycoprotein that is the main component of mucus in the digestive and respiratory tracts. Adequate mucin is essential for gut health, as it protects the intestinal lining and aids in digestion.
Metabolic Functions:
It plays a role in fat metabolism by helping to prevent the buildup of fat in the liver.
It is a precursor (a starting material) for the synthesis of other important amino acids, such as glycine and serine, which are involved in neurotransmitter function, muscle growth, and immune system support.
Immune System Support: It is important for the production of antibodies and the proper functioning of the immune system.
Since it's essential, you must get L-Threonine from food. It is found in a wide variety of protein-rich foods.
Excellent dietary sources include:
Meat and Poultry: Chicken, turkey, beef, pork, lamb
Fish and Seafood: Tuna, salmon, shrimp, sardines
Dairy Products: Cottage cheese, yogurt, milk, cheese
Eggs
Nuts and Seeds: Pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, peanuts, almonds
Legumes: Lentils, black beans, chickpeas, soybeans and tofu
Whole Grains: Wheat germ, quinoa
For most people eating a balanced diet with adequate protein, threonine deficiency is very rare.
While deficiency is uncommon, L-Threonine is available as a dietary supplement in powder or capsule form. Its use is often targeted for specific conditions:
Digestive Health: Due to its role in mucin production, it is sometimes supplemented to support gut health and manage conditions like leaky gut syndrome or ulcerative colitis, though more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Muscle Spasticity (MS): Some studies have explored its use for reducing muscle spasticity in patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS), with mixed results.
Athletics and Bodybuilding: Like other amino acids, it is sometimes used in supplements aimed at promoting muscle growth and recovery, though its direct impact is less pronounced than that of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
Deficiency: True deficiency is unlikely with a normal diet. Symptoms could include:
Digestive upset
Emotional agitation
Confusion
Fatty liver disease (in severe cases)
Safety and Side Effects: L-Threonine is generally considered safe when consumed from food. In supplemental form, high doses may cause minor side effects such as stomach upset, nausea, or headache. As with any supplement, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting, especially for individuals with liver or kidney conditions.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Classification | Essential Amino Acid |
| Primary Role | Building block for proteins, especially structural proteins like collagen and elastin |
| Key Function | Critical for gut health via production of mucin |
| Dietary Sources | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Supplement Use | Gut health, muscle spasticity (research ongoing), athletics |
| Deficiency | Very rare with a normal diet |
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or taking new supplements.




Used as a nutritional supplement.

Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية