Search

Search

-Asparagine_monohydrate主图.jpg)




-Asparagine_monohydrate主图.jpg)




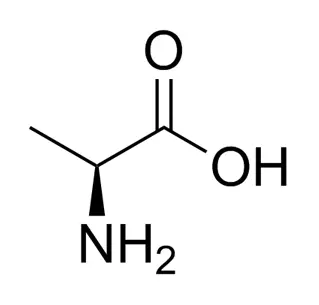
D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate is the non-proteinogenic, mirror-image isomer of the common amino acid L-asparagine, crystallized with one water molecule. Unlike the L-form used in proteins, this D-isomer is rare in nature and not incorporated into proteins during synthesis. It serves specialized roles in bacterial cell walls and as a potential neuromodulator in the brain. Primarily, it is used as a crucial reagent in biochemical research to study the functions of D-amino acids and as a standard in chiral chromatography for separating amino acid isomers.
D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate is a specific stereoisomer of the amino acid asparagine, crystallized with one molecule of water. To break down its name:
Asparagine (Asn, N): This is one of the 20 common amino acids that form the building blocks of proteins. It was the first amino acid to be isolated (from asparagus juice, hence its name). It is classified as a neutral, polar amino acid due to the amide group in its side chain.
D-(-): This prefix is crucial. It specifies the molecule's chirality, or "handedness."
Most amino acids found in proteins are the L- stereoisomer. L-Asparagine is the biologically active form used by living organisms in protein synthesis and metabolism.
D-Asparagine is the mirror-image molecule. It is not incorporated into proteins by the standard cellular machinery and is relatively rare in nature. The (-) indicates it is levorotatory, meaning it rotates plane-polarized light to the left.
Monohydrate: This means the crystalline form of this D-Asparagine molecule has one molecule of water (H₂O) associated with it per molecule of asparagine. This water of hydration helps stabilize the crystal structure.
Chemical Formula: C₄H₈N₂O₃ · H₂O
Appearance: Typically a white, crystalline powder.
Solubility: Generally soluble in water.
Biological Role: Unlike its L-counterpart, D-Asparagine is not a primary building block for proteins. However, it is found in some specific biological contexts:
It is present in certain bacterial cell walls and some antibiotics.
It has been identified in the human brain and other tissues, where it is believed to play a role in neuroendocrine and nervous system function, potentially acting as a neurotransmitter or neuromodulator.
| Feature | D-(-)-Asparagine | L-Asparagine |
|---|---|---|
| Stereochemistry | "Right-handed" mirror image | "Left-handed," the standard form |
| Biological Role | Non-proteinogenic; specialized roles | Proteinogenic (builds proteins); key in metabolism |
| Metabolism | Not metabolized by standard pathways | Incorporated into proteins and central to nitrogen metabolism |
| Prevalence | Rare in nature | Abundant in all life forms |
Biochemical Research: It is primarily used as a research reagent.
To study the specific biological functions and pathways of D-amino acids in the nervous system and endocrine system.
To investigate enzymes that interact with D-amino acids.
Used as a standard in analytical chemistry (e.g., chiral chromatography) to separate and identify different amino acid isomers.
Cell Culture: It may be used in specific microbial culture media.
Food and Feed Additive: While less common, it can be used in specialized applications.
In summary, D-(-)-Asparagine monohydrate is the non-proteinogenic, mirror-image form of the common amino acid asparagine, supplied as a stable crystalline hydrate, and is most importantly used as a tool in scientific research to understand the unique roles of D-amino acids in biology.




Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية