Search

Search











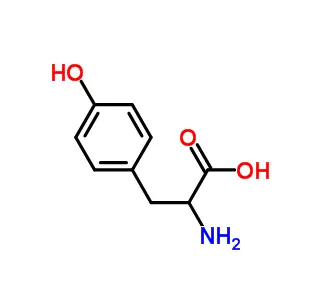
D-Methionine is the mirror-image form of the essential amino acid L-Methionine. Unlike the natural L-form used in human proteins, D-Methionine cannot be directly incorporated into proteins. However, the human body can partially convert it into usable L-Methionine. Its primary use is in animal feed (especially poultry), often as part of a DL-Methionine blend (50/50 D and L), providing a cost-effective methionine source. It's researched for potential radioprotection during cancer therapy, but is not a standard human supplement; L-Methionine is preferred for human nutrition.
D-Methionine is one of the two stereoisomers (mirror-image forms) of the essential amino acid methionine. Here's a breakdown of what it is and its key characteristics:
Stereoisomers:
Amino acids (except glycine) exist in two mirror-image forms: L-form and D-form.
L-Methionine is the "left-handed" form. This is the naturally occurring form found in proteins and used by the human body for protein synthesis and various metabolic functions. It's an essential amino acid, meaning we must get it from our diet.
D-Methionine is the "right-handed" form. It is the mirror image of L-Methionine.
Biological Activity & Use:
Not Used in Protein Synthesis: The human body (and most living organisms) primarily uses L-amino acids to build proteins. Enzymes involved in protein synthesis specifically recognize the L-form. Therefore, D-Methionine cannot be directly incorporated into human proteins.
Limited Metabolic Use (Requires Conversion): While D-Methionine itself isn't directly usable for protein building, mammals (including humans) possess an enzyme called D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO). This enzyme can convert D-Methionine into its corresponding α-keto acid, which can then potentially be converted (transaminated) back into L-Methionine.
Bioavailability: Because of this conversion pathway, D-Methionine can provide a source of L-Methionine for the body, although it's generally considered less bioavailable and efficient than directly consuming L-Methionine. Studies show it has about 25-70% of the biological value of L-Methionine in humans and animals.
Animal Feed Supplement: The primary commercial use of D-Methionine is in animal nutrition, specifically poultry and swine feed. It's often used as part of a racemic mixture (DL-Methionine - a 50/50 blend of D and L forms). Since animals (like chickens) can also convert the D-form to the L-form, DL-Methionine is a cost-effective way to supplement dietary methionine, promoting growth and feed efficiency. Pure D-Methionine is also used in some specific feed formulations.
Other Potential Uses/Research:
Radioprotection: Some research (primarily animal studies) has explored D-Methionine's potential to protect against radiation damage to healthy tissues (like salivary glands and oral mucosa) during cancer radiotherapy. Its mechanism might involve antioxidant properties or modulating cellular metabolism.
Ototoxicity Protection: Studies have investigated whether D-Methionine can help protect against hearing loss caused by certain chemotherapy drugs (like cisplatin) or antibiotics (like aminoglycosides).
Research Tool: D-Methionine is used in biochemical and pharmacological research to study amino acid metabolism, transport, and the effects of D-amino acids.
Toxicity & Safety:
D-Methionine is generally considered low in toxicity when consumed at appropriate levels, primarily because it can be converted to the useful L-form. However, very high doses could potentially overwhelm the conversion system or lead to imbalances.
It is NOT a standard human nutritional supplement. L-Methionine is the preferred form for human use. D-Methionine supplements are not common and should only be used under medical supervision if being investigated for specific therapeutic purposes like radioprotection.
In Summary:
D-Methionine is the non-natural mirror image of the essential amino acid L-Methionine. While not directly usable for human protein synthesis, it can be partially converted into the useful L-form by the body. Its main practical application is as a component of DL-Methionine used to supplement methionine in animal feed (especially poultry). It has also been researched for potential protective effects against radiation and drug-induced hearing loss, but it is not a standard human supplement. L-Methionine remains the biologically relevant form for human nutrition.



Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية -Asparagine_monohydrate主图.jpg)
主图.jpg)