Search

Search










Here's a concise overview of D-Tryptophan:
D-Tryptophan (C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₂) is the non-proteinogenic, D-enantiomer of the essential amino acid tryptophan. Its structure features an indole ring linked to an alanine backbone with (R)-configuration at the α-carbon.
Key properties:
White crystalline solid, slightly water-soluble.
Not used in mammalian protein synthesis (unlike natural L-tryptophan).
Metabolized by D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) to D-kynurenine.
Significance:
Research tool: Probes enzyme stereospecificity (e.g., racemases).
Microbial metabolism: Converted to bioactive compounds in gut flora.
Pharmaceuticals: Chiral building block for synthetic peptides/drugs.
Agriculture: Studied in plant defense signaling.
D-Tryptophan (C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₂) is the D-enantiomer of the essential amino acid tryptophan. Here's its key chemical profile:
Molecular Formula: C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₂
Backbone: Features an indole ring (fused benzene+pyrrole) attached to an alanine moiety (α-amino acid group).
Chiral Center: The α-carbon has D-configuration ((R)-stereochemistry), mirroring L-tryptophan.
IUPAC Name: (R)-2-Amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder.
Melting Point: ~285°C (decomposes).
Solubility:
Slightly soluble in water.
Soluble in dilute acids/bases (forms zwitterions).
Optical Activity: Dextrorotatory ([α]D ≈ +33° in water).
Fluorescence: UV-excited blue emission (λₑₘ ~350 nm).
Acid-Base Properties:
Carboxyl group (pKa ~2.4), amino group (pKa ~9.3).
Exists as a zwitterion at physiological pH.
Reactivity:
Indole ring undergoes electrophilic substitution (e.g., halogenation).
Sensitive to light/oxidation (forms kynurenine derivatives).
Unnatural Isomer: Not incorporated into proteins in eukaryotes (unlike L-tryptophan).
Metabolic Role:
Converted to D-kynurenine by gut/liver enzymes.
Potential precursor to bioactive microbial metabolites.
Enzyme Studies: Used to probe stereospecificity of enzymes (e.g., tryptophanase, racemases).
Pharmaceutical Synthesis: Chiral building block for peptidomimetics & antibiotics.
Biochemical Research:
Substrate for studying D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO).
Tool to investigate gut microbiome metabolism.
Agriculture: Investigated in plant signaling (defense responses).
CAS Number: 153-94-6
Key Distinction: Unlike proteinogenic L-tryptophan, D-tryptophan is non-proteinogenic and primarily studied for its unique metabolic interactions and chiral utility.
Summary: A stereospecific, non-natural amino acid with an indole core, valued for its role in enzymology, microbial metabolism, and as a chiral synthon in organic chemistry. Its fluorescence and metabolic pathways make it a probe in biochemical studies.

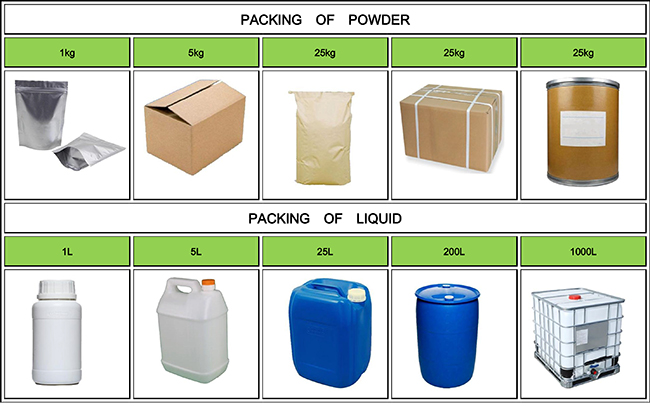


Fortunachem Provides Not Only Professional Chemical Products But Also Professional Help
Keeping you up-to-date with all the latest information, news, and events about Fortunachem!

Quick Links
Add:
E-mail:
 English
English  Español
Español  français
français  العربية
العربية 
-Homoarginine_hydrochloride主图.jpg)



